Glossary
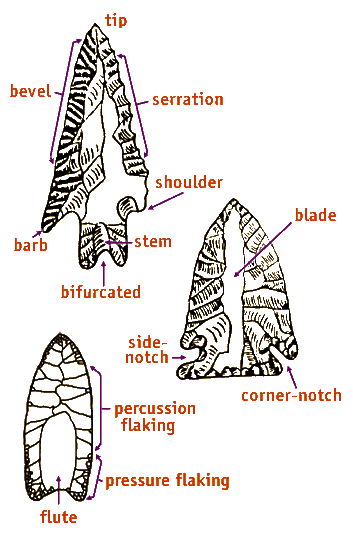
A narrow projection at the junction of the blade and base of a point, often on corner-notched types.
Portion of the point to which the spear or arrow shaft or knife handle was attached.
Formed when blade edge is resharpened by flaking from one side only, creating a definitely angular cross section
Refers to the shape of the cross section of a point or blade; both upper and lower surfaces are convex.
Refers to a point base that is split.
The relatively large portion of a point that includes the cutting edges.
Indentation at the base of a point that is oriented at approximately 45 degree angle to the point's long axis.
Blade edge that curves away from the point's long axis; convex.
A distinctive flake struck from the base toward the tip on one or both faces that flattens the point, making it fit more snugly on a spear shaft.
Blade edge that curves toward the point's long axis, often due to resharpening; concave.
Removing flakes from a piece of flint by directly striking the edge with a hammerstone or a cylindrical piece of antler or wood; the technique generally used to form the initial shape of a tool; resulting flake scars are usually large and irregular in outline.
Removing small flakes by pressing a rounded-end tool such as an antler tine against the edge of a tool; technique used for refining the shape of a tool, resharpening blade edges, forming notches, or other tasks requiring more control than percussion flaking; resulting flake scars are usually small and narrow.
Saw-tooth like projections along the blade edge of a point; presumed to be a form of resharpening most often characteristic of points made by prehistoric Archaic cultures (8000- 500 BC).
Lower corner of the blade portion of a point where it joins the stem.
Indentation at the base of a point that is oriented at approximately 45 degree angle to the point's long axis.
A type of base with straight, un-notched edges.
Pointed end of the blade portion of a point.
